World Economic Forum, Ag Groups Urge More Support for SAF
A new report says industry collaboration, the adaptation of existing infrastructure, greater investment in R&D, and increased public education and public-sector engagement are key to scaling SAF to meet the growing demand.
News & Events
-
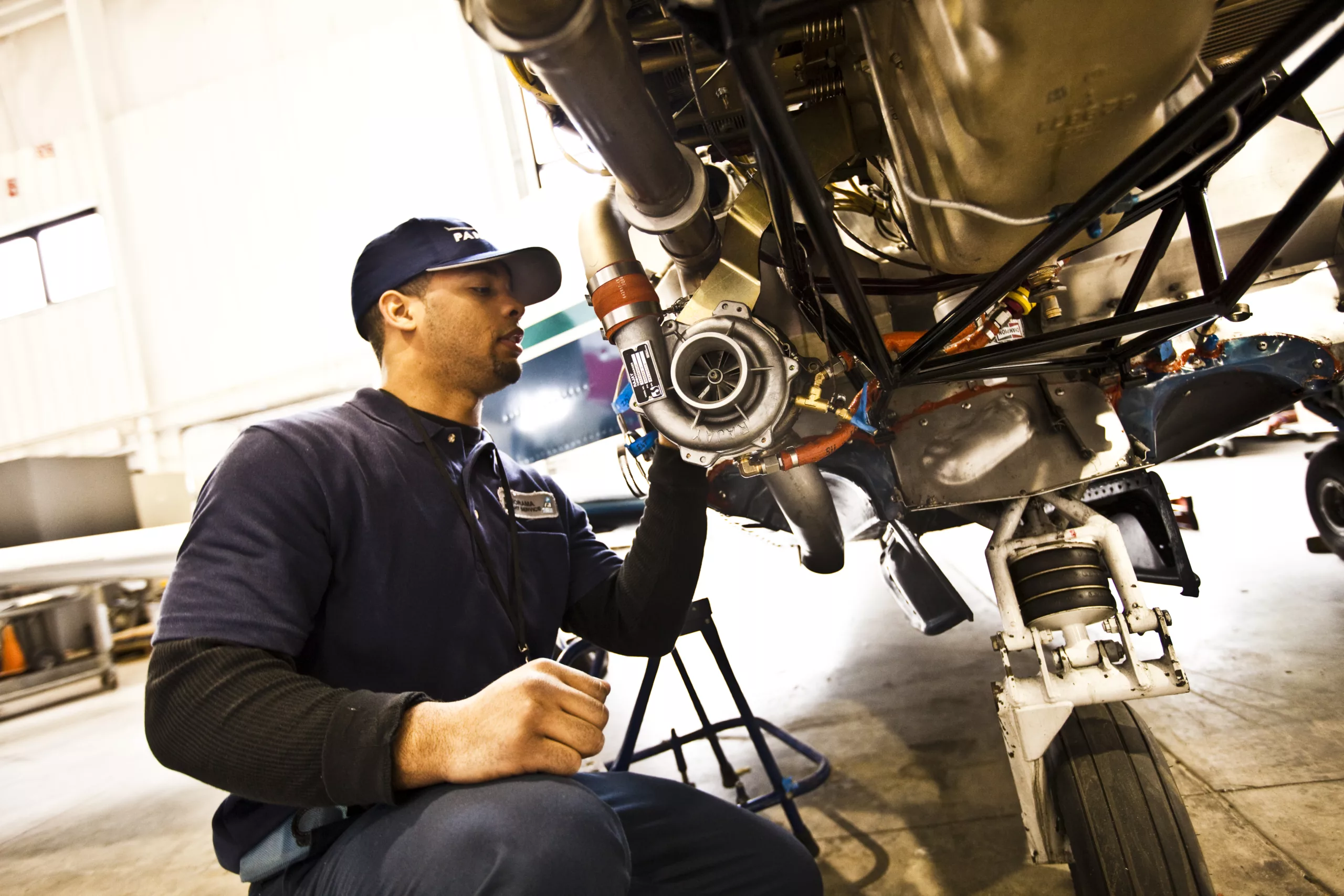

FAA Offers Funding For SAF Infrastructure Projects At Airports
Learn more: FAA Offers Funding For SAF Infrastructure Projects At Airports -
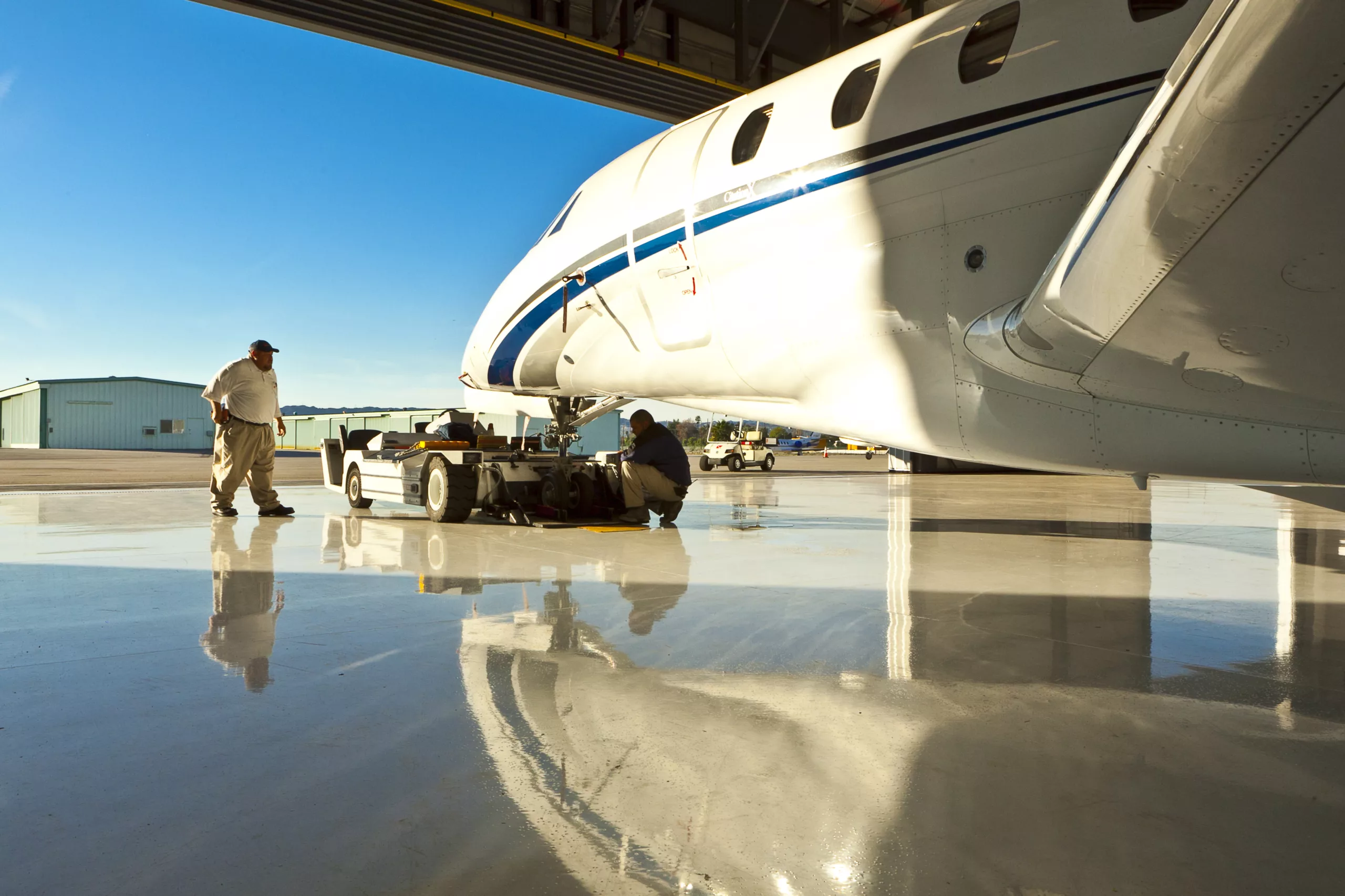

The Top Technological Advancements Driving The Aviation Industry
Learn more: The Top Technological Advancements Driving The Aviation Industry -
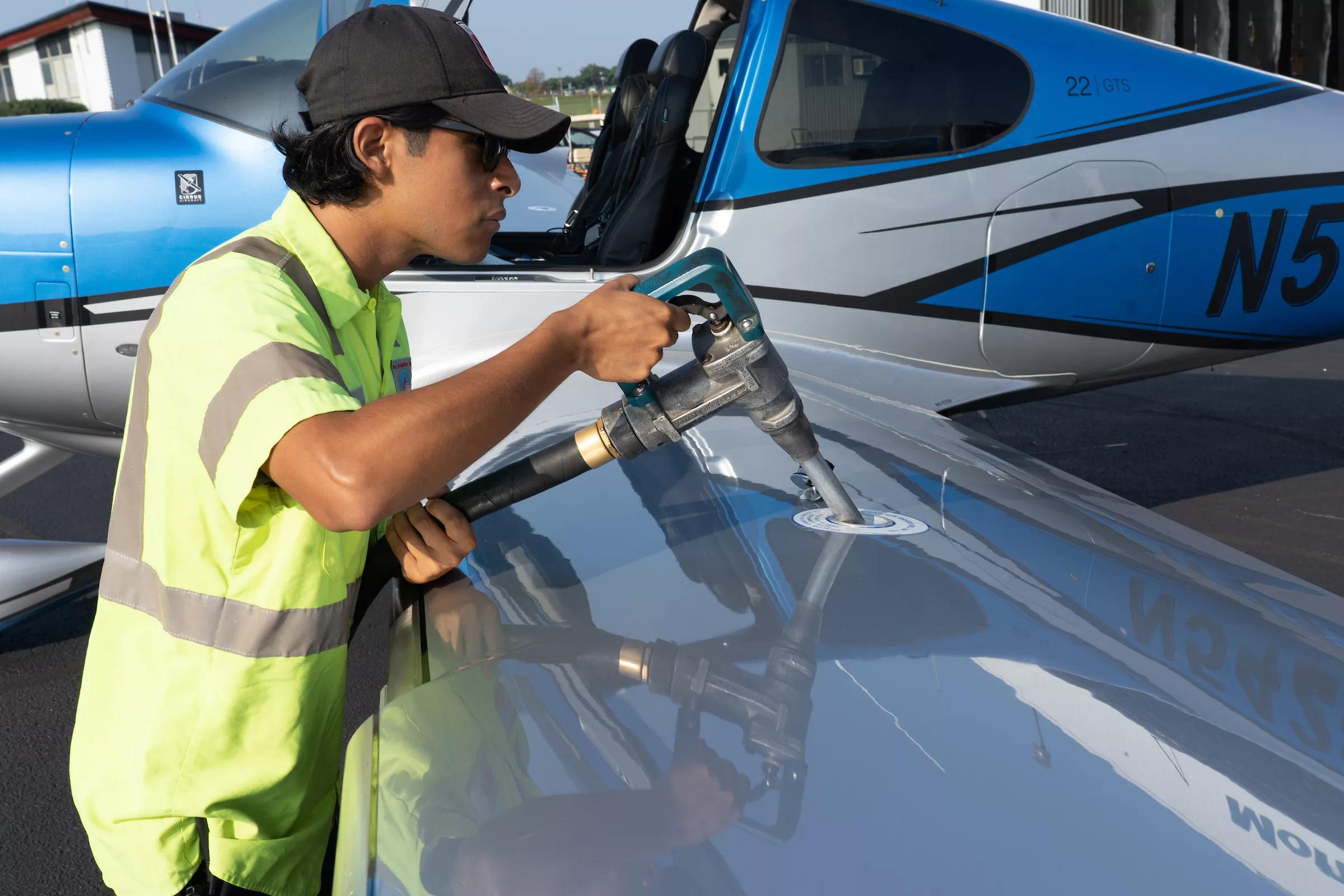

Phillips 66 Begins Commercial Operations At Rodeo Biorefinery
Learn more: Phillips 66 Begins Commercial Operations At Rodeo Biorefinery -
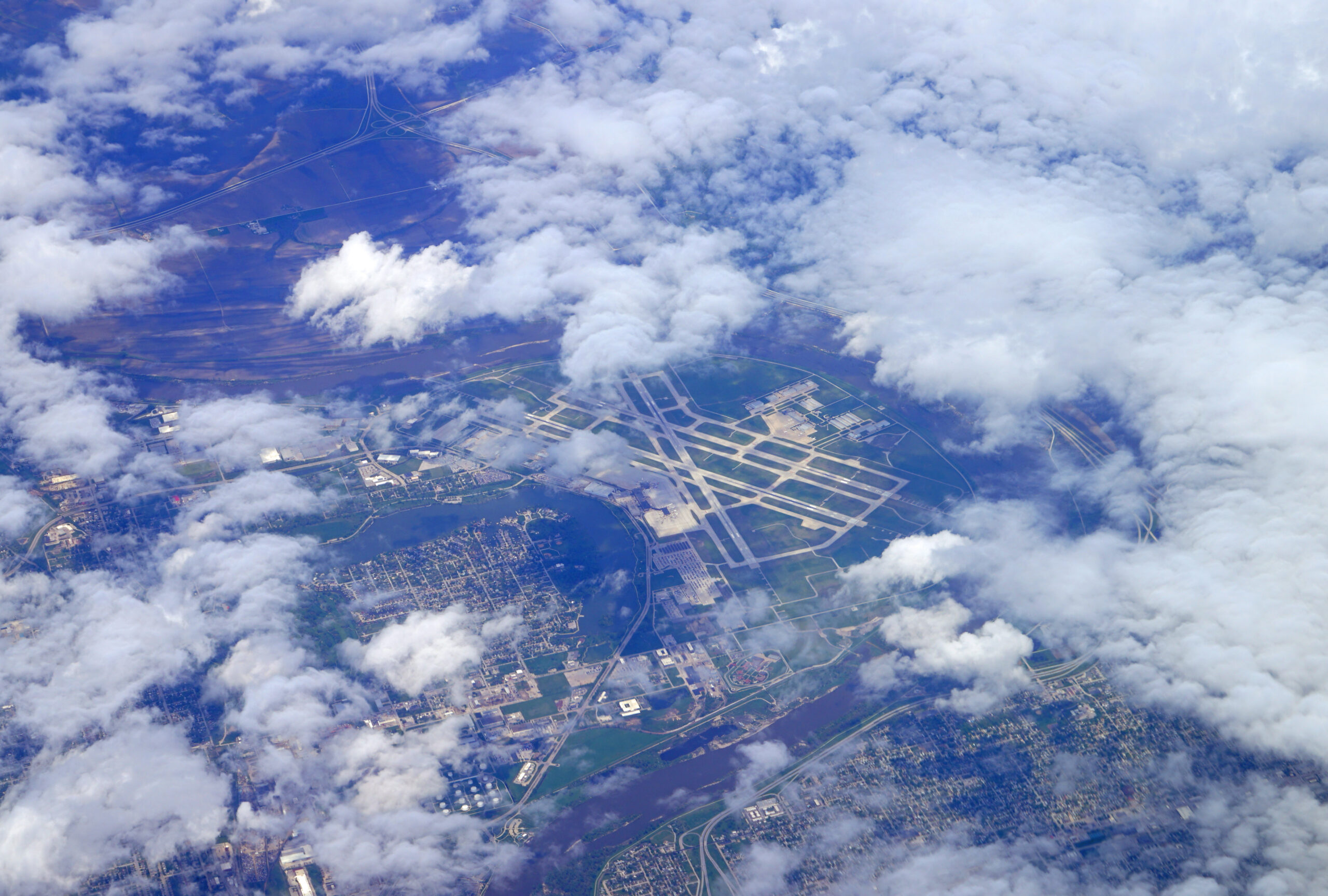

Global Business Jet Market 2024-2027 Sees Sustainability as Top Priority
Learn more: Global Business Jet Market 2024-2027 Sees Sustainability as Top Priority -

World Economic Forum, Ag Groups Urge More Support for SAF
Learn more: World Economic Forum, Ag Groups Urge More Support for SAF -

Exxon Says US Jet Fuel Policy Is Needed to Boost Investment
Learn more: Exxon Says US Jet Fuel Policy Is Needed to Boost Investment -

Michigan Bill Would Incentivize SAF Production
Learn more: Michigan Bill Would Incentivize SAF Production -

World Energy Eyes $2BN DOE Loan for Houston Plant
Learn more: World Energy Eyes $2BN DOE Loan for Houston Plant -

DOE Says Tripling Biomass Production Can Allow US to Decarbonize Aviation
Learn more: DOE Says Tripling Biomass Production Can Allow US to Decarbonize Aviation

About Us
The Business Aviation Coalition for Sustainable Aviation Fuel, developed by a coalition of international aviation organizations, was created to address a “knowledge gap” on the availability and safety of SAF and advance the proliferation of alternative jet fuels at all the logical touchpoints: the manufacturers, the ground handlers and the operators, at the regional, national and international levels.

Commitments
The Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Initiative focuses on emissions reduction through investment and innovation. The industry’s commitment to emissions reduction was further codified through the Business Aviation Commitment on Climate Change, with three aspirational goals contained in the commitment:
average improvement in efficiency per year from 2020 to 2030
Carbon neutral growth from 2020 onwards
in carbon emissions by 2050
Goals
The business aviation community has long been committed to reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from aircraft, with a proven record of advances in carbon reduction. The industry has continually promoted investment in, and development of, innovative products, procedures and policies aimed at reducing its environmental footprint.
Our goals will be met through advancements in four pillars.
An Ambitious Plan to Achieve Sustainable Aviation
The Business Aviation Commitment on Climate Change is the industry’s bold blueprint to cut carbon emissions in half by 2050. In the BACCC, business aviation pledged to achieve carbon-neutral growth after 2020, continue to increase fuel efficiency 2% per year and reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
Continually Working Toward a Lower-Carbon Future
Fueling the Future is an educational and informational resource guide created by the SAF Coalition about the practicalities of SAF development, industry adoption, and pending expansion of supply and use, primarily from the perspectives of the business aviation community. Check out Fueling the Future to learn about the many benefits of SAF and how to get access to safe, sustainable fuel today.
Other Resources
THE BUSINESS AVIATION COALITION FOR SUSTAINABLE AVIATION FUEL STEERING COMMITTEE:
- Air BP
- Alder Fuels
- Atlantic Aviation
- Avfuel
- Bombardier Business Aircraft
- Dassault Falcon Jet
- Embraer Executive Aircraft
- Gulfstream Aerospace
- Jet Aviation
- Neste
- Phillips 66
- Rolls-Royce
- Signature Flight Support/EPIC
- World Energy
- World Fuel Services









